Code
HCS22079
Weight
2.8 Kg / 6.17 lbs
Size
Height
24cm (9") Width
18cm (7") Depth
18cm (7") Material
Copper and Gold
Availability
Available
Date Added
2020-12-25 02:04:00
Note : We used to sell this product 5 years ago so it may no longer be in our stock.
It is possible that we still have it with our suppliers but the price could be different from before.
Feel free to order. We will verify availability and inform you promptly.
It is possible that we still have it with our suppliers but the price could be different from before.
Feel free to order. We will verify availability and inform you promptly.

Safe Payment
We accept Paypal, Money Transfer, Bank Transfer
Confidence
Protection covers your purchase and personal data.
Worldwide Delivery
We ship Worldwide, except Russia.Shipping cost US$25.2 for upto 0.5 kgs

Hotline
Talk to help line for your question on 9841267335About Sacred Serenity Collection
This is a beautiful old Buddhist statue that carries a deep sense of spirituality and craftsmanship. These statues were made around 15 to 20 years ago and are crafted from pure copper. If the statue has gold, it has a thick layer of gold plating, unlike modern statues where using a lot of gold is expensive.
Skilled artisans, who were well-versed in religious teachings, made these statues. They followed traditional guidelines and sacred texts to create each statue with precise expressions and postures. The artisans believed they were creating representations of gods rather than just ordinary figures. This unique perspective is reflected in the statues themselves. Read More . . .
This is a beautiful old Buddhist statue that carries a deep sense of spirituality and craftsmanship. These statues were made around 15 to 20 years ago and are crafted from pure copper. If the statue has gold, it has a thick layer of gold plating, unlike modern statues where using a lot of gold is expensive.
Skilled artisans, who were well-versed in religious teachings, made these statues. They followed traditional guidelines and sacred texts to create each statue with precise expressions and postures. The artisans believed they were creating representations of gods rather than just ordinary figures. This unique perspective is reflected in the statues themselves. Read More . . .
Partly Gold plating.
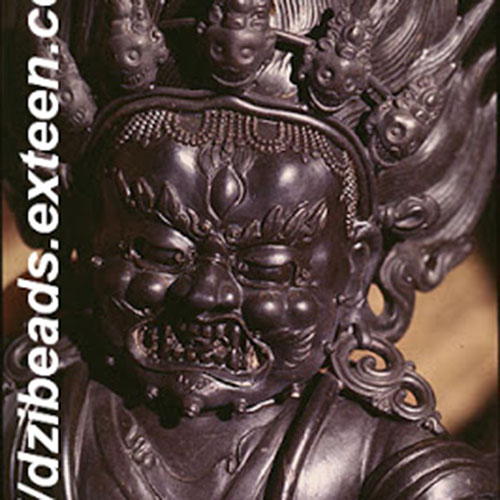
This [old], Statue Of Karmapa, [partly Gold Plated] has a Partly gold-plated finish. Partly fire gold gilding, a common practice in Nepali handicrafts. This technique is skillfully employed by artisans to create intricate designs on various metal objects, including statues, jewelry, and decorative items. Through a process, a mask or resist is applied to safeguard specific areas from the gold plating. The object is then subjected to high temperatures, allowing the gold to beautifully adhere to exposed surfaces using a combination of heat and pressure.
In the realm of Buddhist statues, this technique holds additional significance as it distinguishes the golden-plated body from the oxidized or maroon-painted clothing. This visual separation conveys the contrast between the divine purity of the body and the modest attire symbolizing the humble lifestyle of Buddhist monks. The partly fire gold gilding not only adds exquisite detail and elegance but also embodies the deep cultural and spiritual meaning associated with these treasured artifacts. Read More . . .
This [old], Statue Of Karmapa, [partly Gold Plated] has a Partly gold-plated finish. Partly fire gold gilding, a common practice in Nepali handicrafts. This technique is skillfully employed by artisans to create intricate designs on various metal objects, including statues, jewelry, and decorative items. Through a process, a mask or resist is applied to safeguard specific areas from the gold plating. The object is then subjected to high temperatures, allowing the gold to beautifully adhere to exposed surfaces using a combination of heat and pressure.
In the realm of Buddhist statues, this technique holds additional significance as it distinguishes the golden-plated body from the oxidized or maroon-painted clothing. This visual separation conveys the contrast between the divine purity of the body and the modest attire symbolizing the humble lifestyle of Buddhist monks. The partly fire gold gilding not only adds exquisite detail and elegance but also embodies the deep cultural and spiritual meaning associated with these treasured artifacts. Read More . . .
Gold Painted Face
The face of [old], Statue Of Karmapa, [partly Gold Plated] is painted with gold to enhance its significant features, particularly the eyes, and lips. This detailed painting is essential as it brings forth the crucial attributes of the expression of eyes and lips that metal carving alone cannot capture.
Moreover, the painted face serves as a symbolic and sacred ritual in Buddhism, preparing the statue for consecration and practice. The act of painting the face with gold in Buddhism holds deep meaning. It represents the intention to bring life and expression to the statue, imbuing it with a sense of vitality and presence. The application of gold on the face showcases the devotion and craftsmanship of the artisans, ensuring that every detail is carefully attended to honor the sacred essence of the [old], Statue Of Karmapa, [partly Gold Plated]. Read More . . .
The face of [old], Statue Of Karmapa, [partly Gold Plated] is painted with gold to enhance its significant features, particularly the eyes, and lips. This detailed painting is essential as it brings forth the crucial attributes of the expression of eyes and lips that metal carving alone cannot capture.
Moreover, the painted face serves as a symbolic and sacred ritual in Buddhism, preparing the statue for consecration and practice. The act of painting the face with gold in Buddhism holds deep meaning. It represents the intention to bring life and expression to the statue, imbuing it with a sense of vitality and presence. The application of gold on the face showcases the devotion and craftsmanship of the artisans, ensuring that every detail is carefully attended to honor the sacred essence of the [old], Statue Of Karmapa, [partly Gold Plated]. Read More . . .
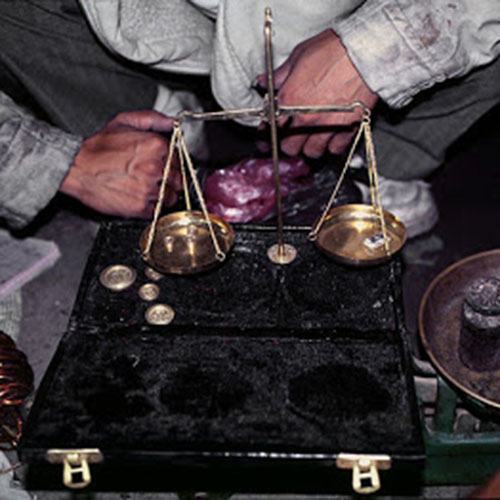
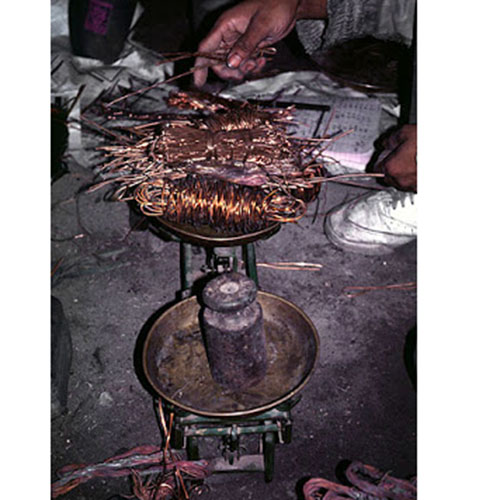
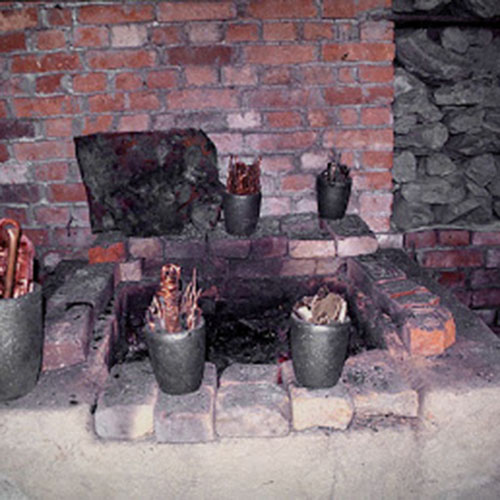
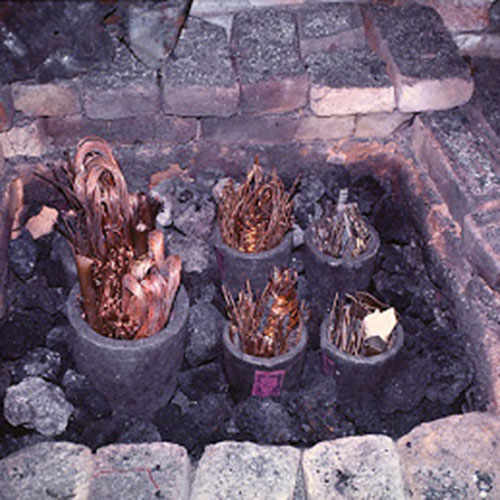
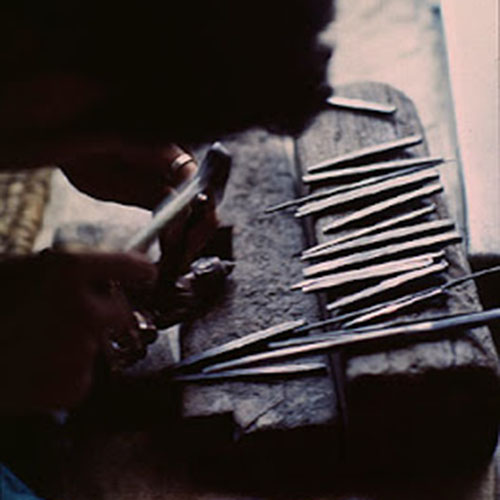
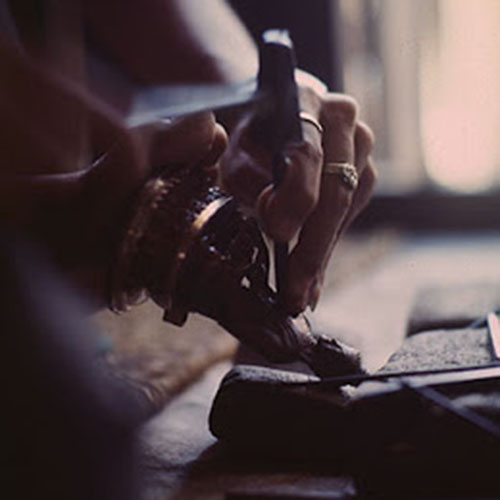
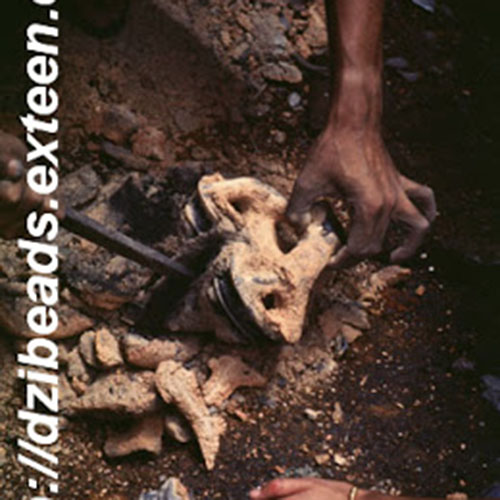
Lost-Wax System
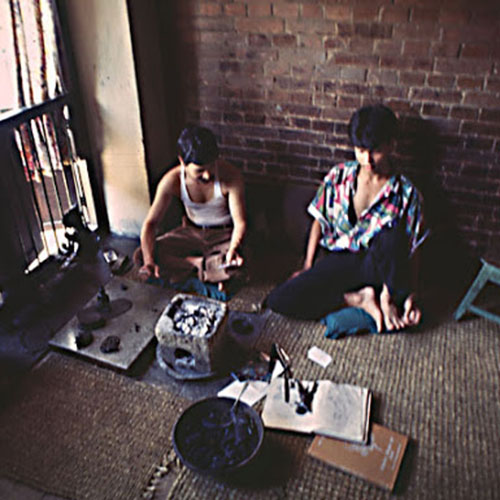
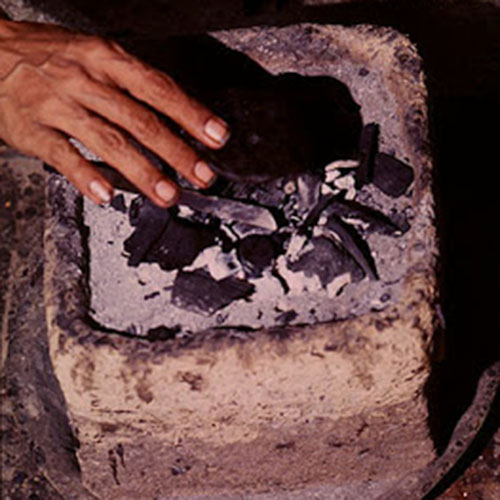
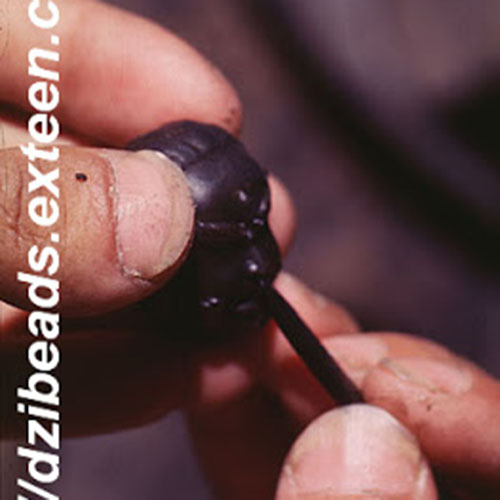
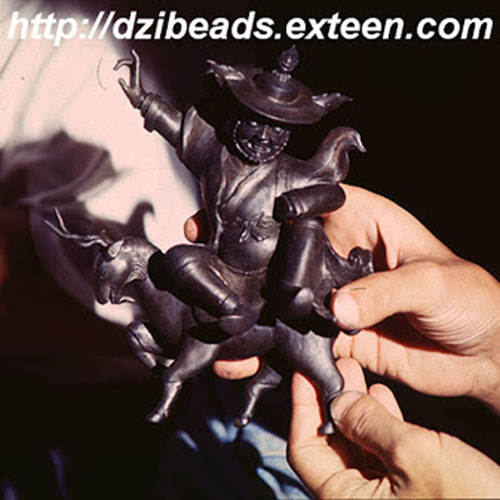
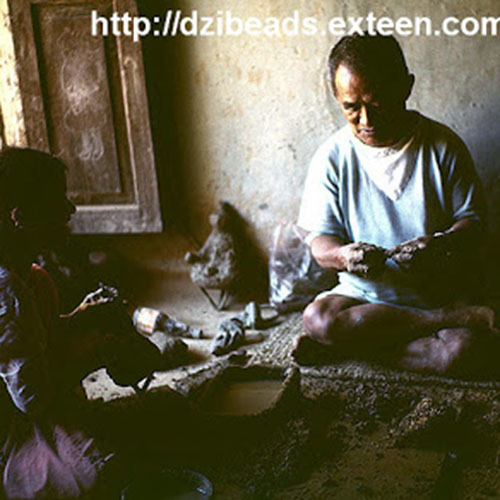
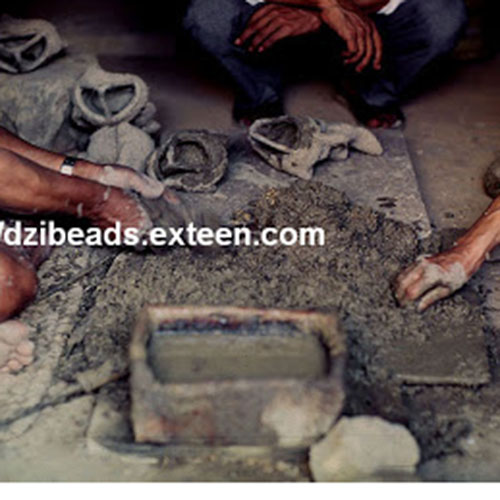
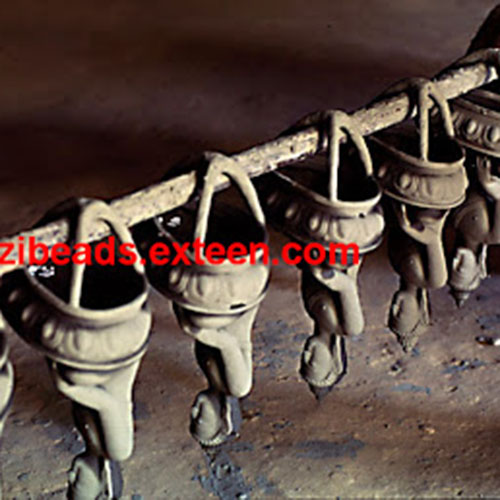
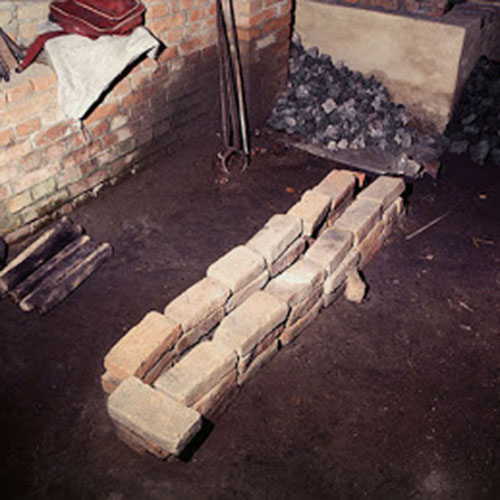
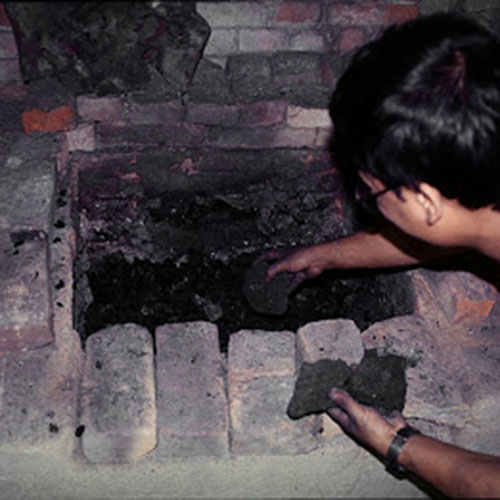
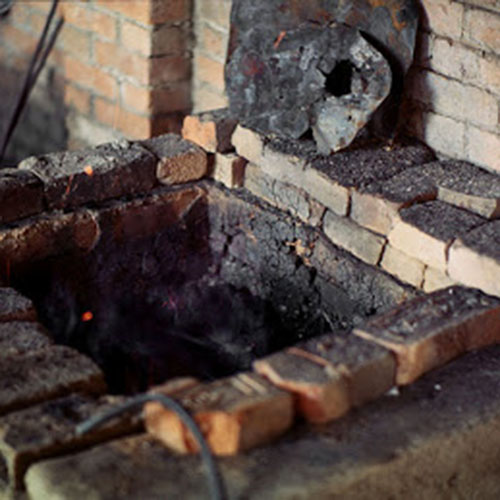
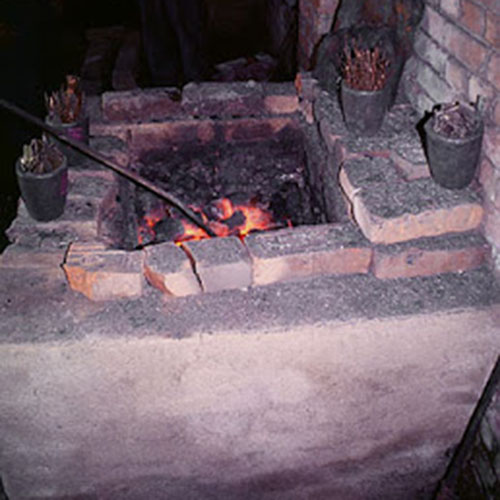
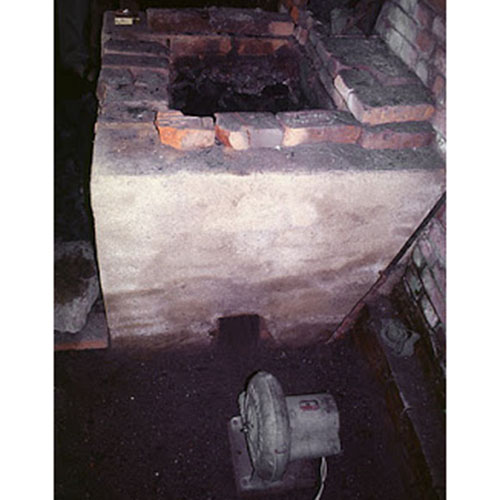
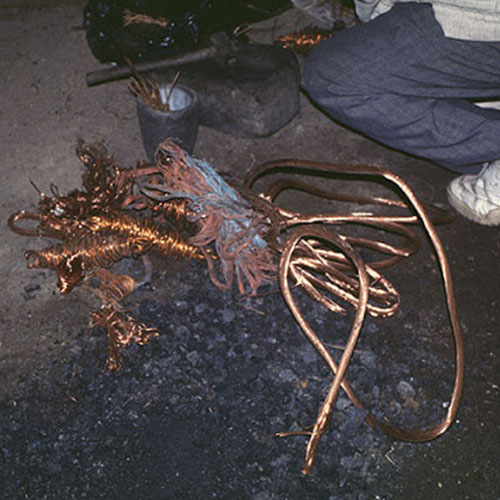
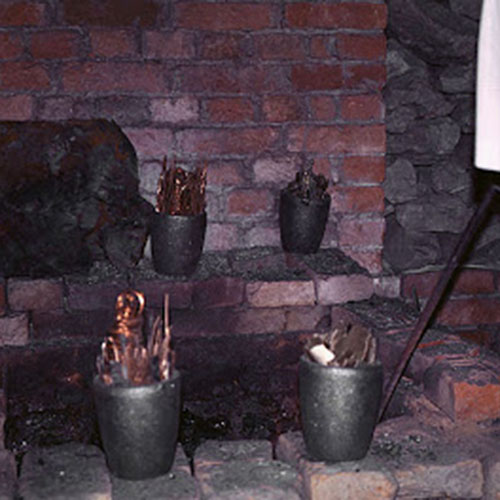
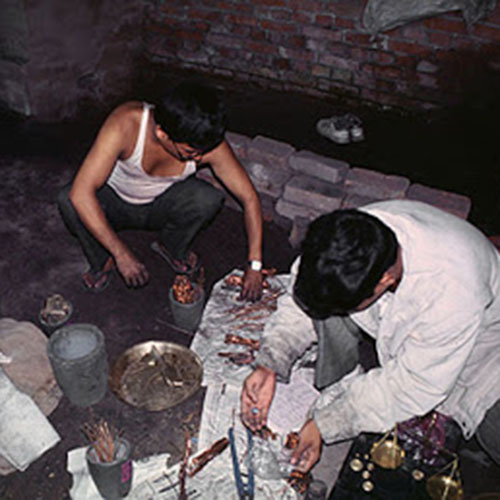
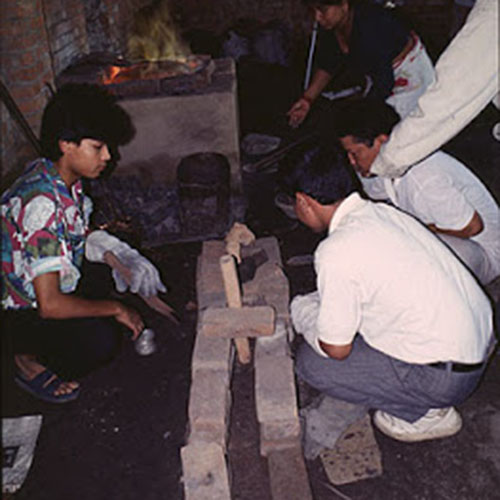
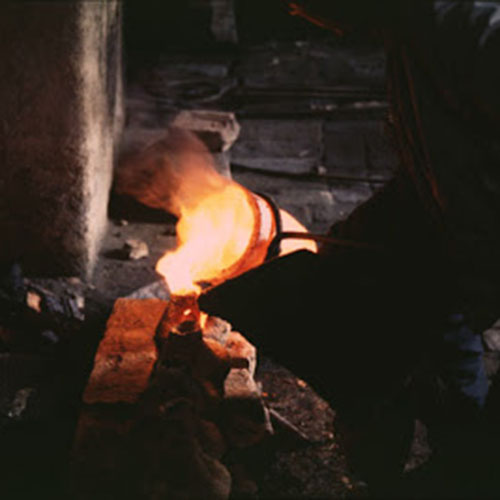
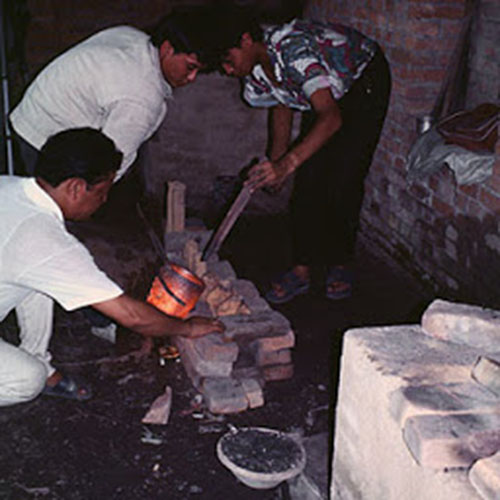
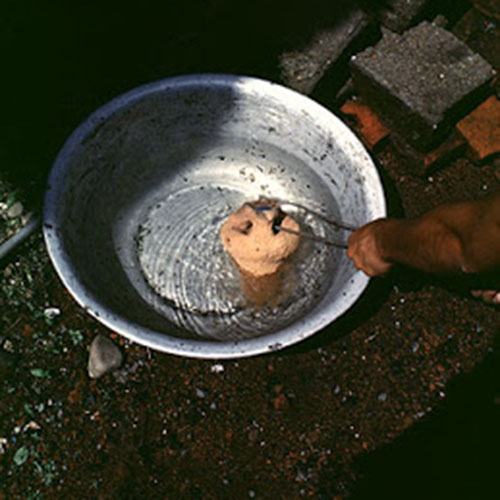
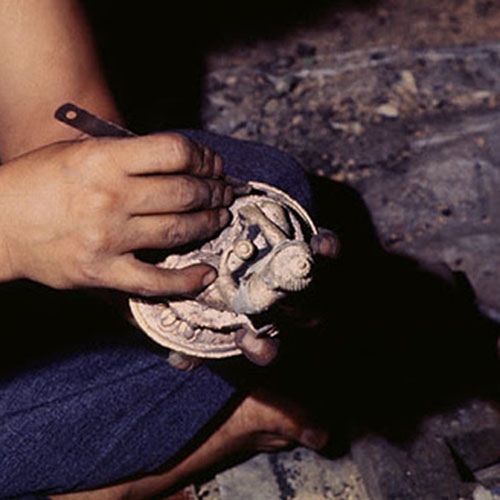
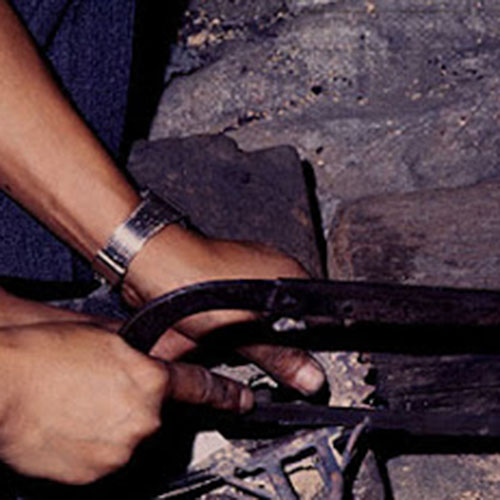
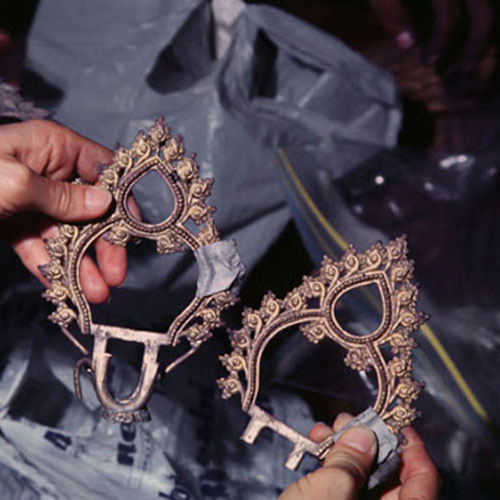
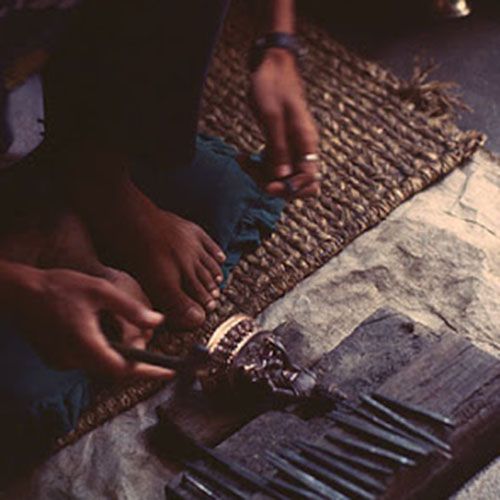
This Collection of [old], Statue Of Karmapa, [partly Gold Plated] is made by the process of the Lost Wax system. This is a very complicated, time consuming and historic process of making metal sculptures.Which is why it is sometimes called Precision Casting as well. Hence the sculptures made by this process are comparatively expensive. There are many new, advanced and less time consuming methods of casting metal sculptures available as well. But due to the benefits provided by the traditional lost wax system in quality control and customization, we prefer the Loss wax system over Ceramic molding, or sand casting to make our Collection.
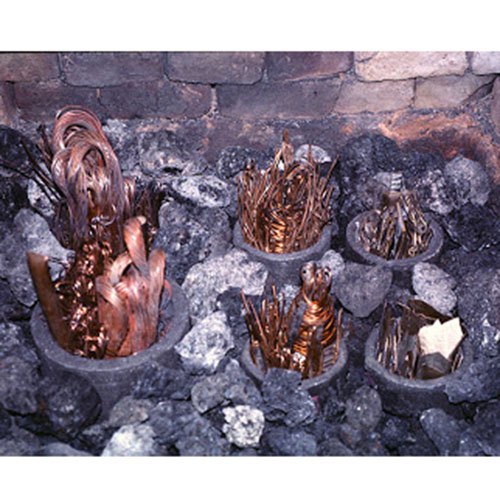
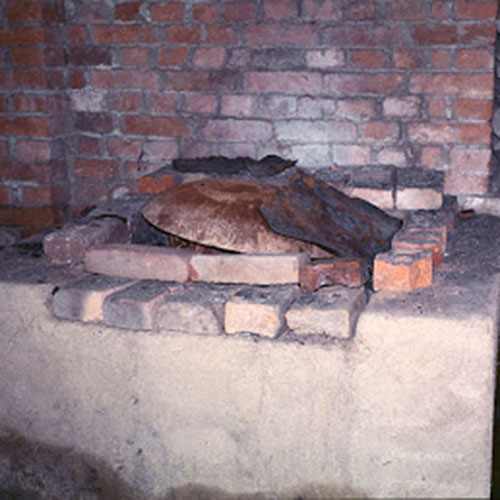
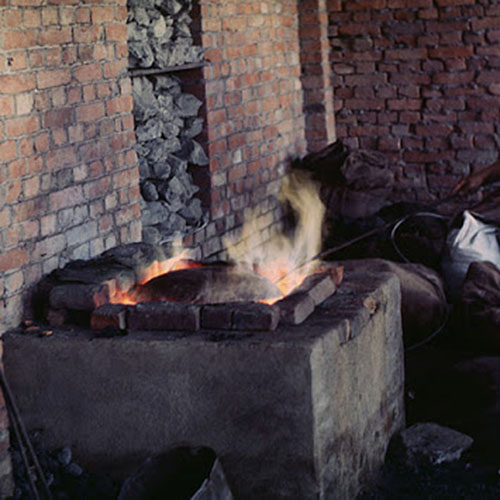
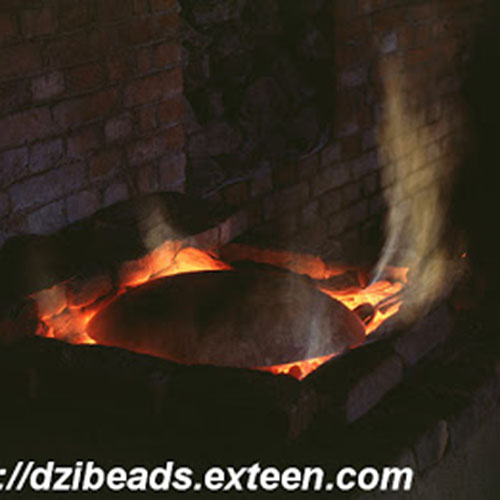
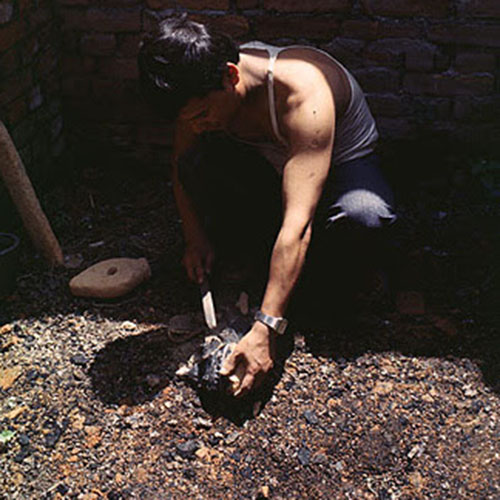
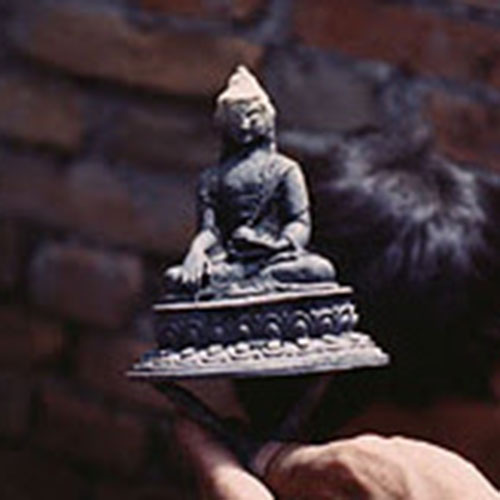
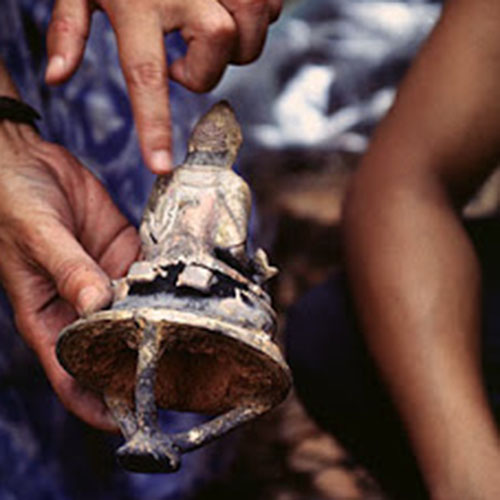
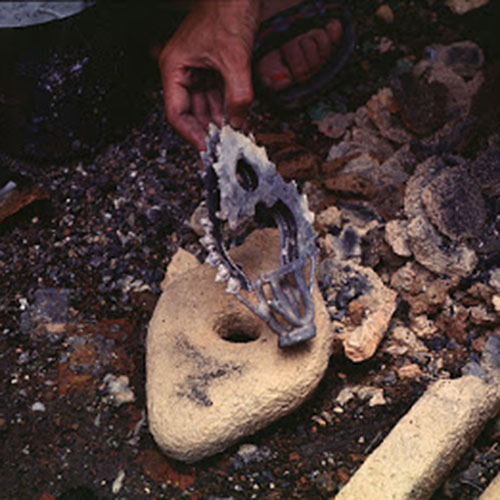
Below we have tried to illustrate the process of making a loss wax system statue: Read More . . .
This Collection of [old], Statue Of Karmapa, [partly Gold Plated] is made by the process of the Lost Wax system. This is a very complicated, time consuming and historic process of making metal sculptures.Which is why it is sometimes called Precision Casting as well. Hence the sculptures made by this process are comparatively expensive. There are many new, advanced and less time consuming methods of casting metal sculptures available as well. But due to the benefits provided by the traditional lost wax system in quality control and customization, we prefer the Loss wax system over Ceramic molding, or sand casting to make our Collection.
Below we have tried to illustrate the process of making a loss wax system statue: Read More . . .
Brief Introduction :
The Karmapa (honorific title His Holiness the Gyalwa (རྒྱལ་བ་, Victorious One) Karmapa, more formally as Gyalwang (རྒྱལ་དབང་ཀརྨ་པ་, King of Victorious Ones) Karmapa, and informally as the Karmapa Lama) is the head of the Karma Kagyu, the largest sub-school of the Kagyu (བཀའ་བརྒྱུད, Wylie: bka' brgyud), itself one of the four major schools of Tibetan Buddhism.
The historical seat of the Karmapas is Tsurphu Monastery in the Tolung valley of Tibet. The Karmapa's principal seat in exile is the Dharma Chakra Centre at Rumtek Monastery in Sikkim, India. His regional monastic seats are Karma Triyana Dharmachakra in New York and Dhagpo Kagyu Ling in Dordogne, France.
Due to a controversy within the Karma Kagyu school over the recognition process, the identity of the current 17th Karmapa is disputed by some.
Origin of the lineage :The historical seat of the Karmapas is Tsurphu Monastery in the Tolung valley of Tibet. The Karmapa's principal seat in exile is the Dharma Chakra Centre at Rumtek Monastery in Sikkim, India. His regional monastic seats are Karma Triyana Dharmachakra in New York and Dhagpo Kagyu Ling in Dordogne, France.
Due to a controversy within the Karma Kagyu school over the recognition process, the identity of the current 17th Karmapa is disputed by some.
Dusum Khyenpa, 1st Karmapa Lama (Wylie: Dus gsum Mkhyen pa, 1110-1193), was a disciple of the Tibetan master Gampopa. A talented child who studied Buddhism with his father from an early age and who sought out great teachers in his twenties and thirties, he is said to have attained enlightenment at the age of fifty while practicing dream yoga. He was henceforth regarded by the contemporary highly respected masters Shakya Śri and Lama Shang as the Karmapa, a manifestation of Avalokiteśvara, whose coming was predicted in the Samadhiraja Sutra and the Laṅkāvatāra Sūtra.
The source of the oral lineage, traditionally traced back to the Buddha Vajradhara, was transmitted to the Indian master of mahamudra and tantra called Tilopa (989-1069), through Naropa (1016-1100) to Marpa Lotsawa and Milarepa. These forefathers of the Kagyu (Bka' brGyud) lineage are collectively called the "Golden Rosary".
Karma Pakshi, 2nd Karmapa Lama (1204-1283), is often said to be the first person ever recognized and empowered as a tulku (Wylie: sprul sku), a reincarnated lama (bla ma)
Black Crown :The source of the oral lineage, traditionally traced back to the Buddha Vajradhara, was transmitted to the Indian master of mahamudra and tantra called Tilopa (989-1069), through Naropa (1016-1100) to Marpa Lotsawa and Milarepa. These forefathers of the Kagyu (Bka' brGyud) lineage are collectively called the "Golden Rosary".
Karma Pakshi, 2nd Karmapa Lama (1204-1283), is often said to be the first person ever recognized and empowered as a tulku (Wylie: sprul sku), a reincarnated lama (bla ma)
The Karmapas are the holders of the Black Crown (Wylie: Zhwa-nag) and are thus sometimes known as "the Black Hat Lamas". This crown (Wylie: rang 'byung cod pan "self-arisen crown"), is traditionally said to have been woven by the dakinis from their hair and given to the Karmapa in recognition of his spiritual realization. The physical crown displayed by the Karmapas was offered to Deshin Shekpa, 5th Karmapa Lama by the Yongle Emperor of China as a material representation of the spiritual one.
The crown was last known to be located at Rumtek Monastery in Sikkim, the last home of the 16th Karmapa, although that location has been subject to some upheaval since 1993 causing some to worry as to whether or not it is still there. An inventory of items remaining at Rumtek is purported to be something the Indian government is going to undertake in the near future.
List of Karmapas :The crown was last known to be located at Rumtek Monastery in Sikkim, the last home of the 16th Karmapa, although that location has been subject to some upheaval since 1993 causing some to worry as to whether or not it is still there. An inventory of items remaining at Rumtek is purported to be something the Indian government is going to undertake in the near future.
Dusum Khyenpa (དུས་གསུམ་མཁྱེན་པ་) (1110-1193)
Karma Pakshi (ཀརྨ་པཀྵི་) (1204-1283)
Rangjung Dorje (རང་འབྱུང་རྡོ་རྗེ་) (1284-1339)
Rolpe Dorje (རོལ་པའི་རྡོ་རྗེ་) (1340-1383)
Deshin Shekpa (དེ་བཞིན་གཤེགས་པ་)(1384-1415)
Thongwa Donden (མཐོང་བ་དོན་ལྡན་) (1416-1453)
Chodrak Gyatso (ཆོས་གྲགས་རྒྱ་མཚོ་) (1454-1506)
Mikyo Dorje (མི་བསྐྱོད་རྡོ་རྗེ་) (1507-1554)
Wangchuk Dorje (དབང་ཕྱུག་རྡོ་རྗེ་) (1556-1603)
Choying Dorje (ཆོས་དབྱིངས་རྡོ་རྗེ་) (1604-1674)
Yeshe Dorje (ཡེ་ཤེས་རྡོ་རྗེ་) (1676-1702)
Changchub Dorje (བྱང་ཆུབ་རྡོ་རྗེ་) (1703-1732)
Dudul Dorje (བདུད་འདུལ་རྡོ་རྗེ་) (1733-1797)
Thekchok Dorje (ཐེག་མཆོག་རྡོ་རྗེ་) (1798-1868)
Khakyab Dorje (མཁའ་ཁྱབ་རྡོ་རྗེ་) (1871-1922)
Rangjung Rigpe Dorje (རང་འབྱུང་རིག་པའི་རྡོ་རྗེ་) (1924-1981)
Ogyen Trinley Dorje (ཨོ་རྒྱན་འཕྲིན་ལས་རྡོ་རྗེ།) (b. 1985) or Trinley Thaye Dorje (ཕྲིན་ལས་མཐའ་ཡས་རྡོ་རྗེ།)(b. 1983),
Karma Pakshi (ཀརྨ་པཀྵི་) (1204-1283)
Rangjung Dorje (རང་འབྱུང་རྡོ་རྗེ་) (1284-1339)
Rolpe Dorje (རོལ་པའི་རྡོ་རྗེ་) (1340-1383)
Deshin Shekpa (དེ་བཞིན་གཤེགས་པ་)(1384-1415)
Thongwa Donden (མཐོང་བ་དོན་ལྡན་) (1416-1453)
Chodrak Gyatso (ཆོས་གྲགས་རྒྱ་མཚོ་) (1454-1506)
Mikyo Dorje (མི་བསྐྱོད་རྡོ་རྗེ་) (1507-1554)
Wangchuk Dorje (དབང་ཕྱུག་རྡོ་རྗེ་) (1556-1603)
Choying Dorje (ཆོས་དབྱིངས་རྡོ་རྗེ་) (1604-1674)
Yeshe Dorje (ཡེ་ཤེས་རྡོ་རྗེ་) (1676-1702)
Changchub Dorje (བྱང་ཆུབ་རྡོ་རྗེ་) (1703-1732)
Dudul Dorje (བདུད་འདུལ་རྡོ་རྗེ་) (1733-1797)
Thekchok Dorje (ཐེག་མཆོག་རྡོ་རྗེ་) (1798-1868)
Khakyab Dorje (མཁའ་ཁྱབ་རྡོ་རྗེ་) (1871-1922)
Rangjung Rigpe Dorje (རང་འབྱུང་རིག་པའི་རྡོ་རྗེ་) (1924-1981)
Ogyen Trinley Dorje (ཨོ་རྒྱན་འཕྲིན་ལས་རྡོ་རྗེ།) (b. 1985) or Trinley Thaye Dorje (ཕྲིན་ལས་མཐའ་ཡས་རྡོ་རྗེ།)(b. 1983),


![[old], Statue Of Karmapa, [partly Gold Plated]](https://handicraftseller.com/uploads/pics/product/thumb/2020/12/22079.jpg)
![[old], Statue Of Karmapa, [partly Gold Plated]](https://handicraftseller.com/uploads/pics/product/thumb/2020/12/22079_0.jpg)
![[old], Statue Of Karmapa, [partly Gold Plated]](https://handicraftseller.com/uploads/pics/product/thumb/2020/12/22079_1.jpg)
![[old], Statue Of Karmapa, [partly Gold Plated]](https://handicraftseller.com/uploads/pics/product/thumb/2020/12/22079_2.jpg)






































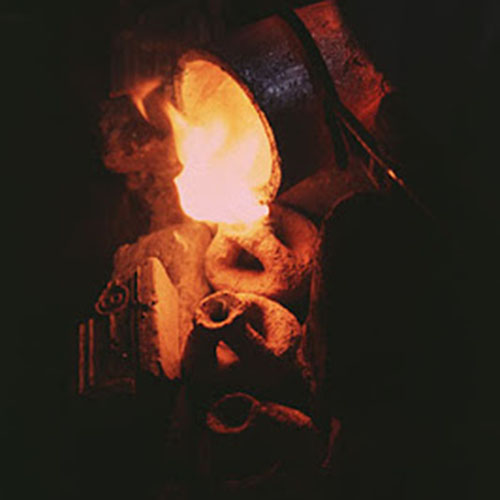


















 Old, Buddhist Statues
Old, Buddhist Statues  Old, Buddhist Statues
Old, Buddhist Statues  Old, Buddhist Handmade Statue
Old, Buddhist Handmade Statue  Old, Buddhist Handmade Statue
Old, Buddhist Handmade Statue  + 50 Year Old Buddhist Miniature Statue
+ 50 Year Old Buddhist Miniature Statue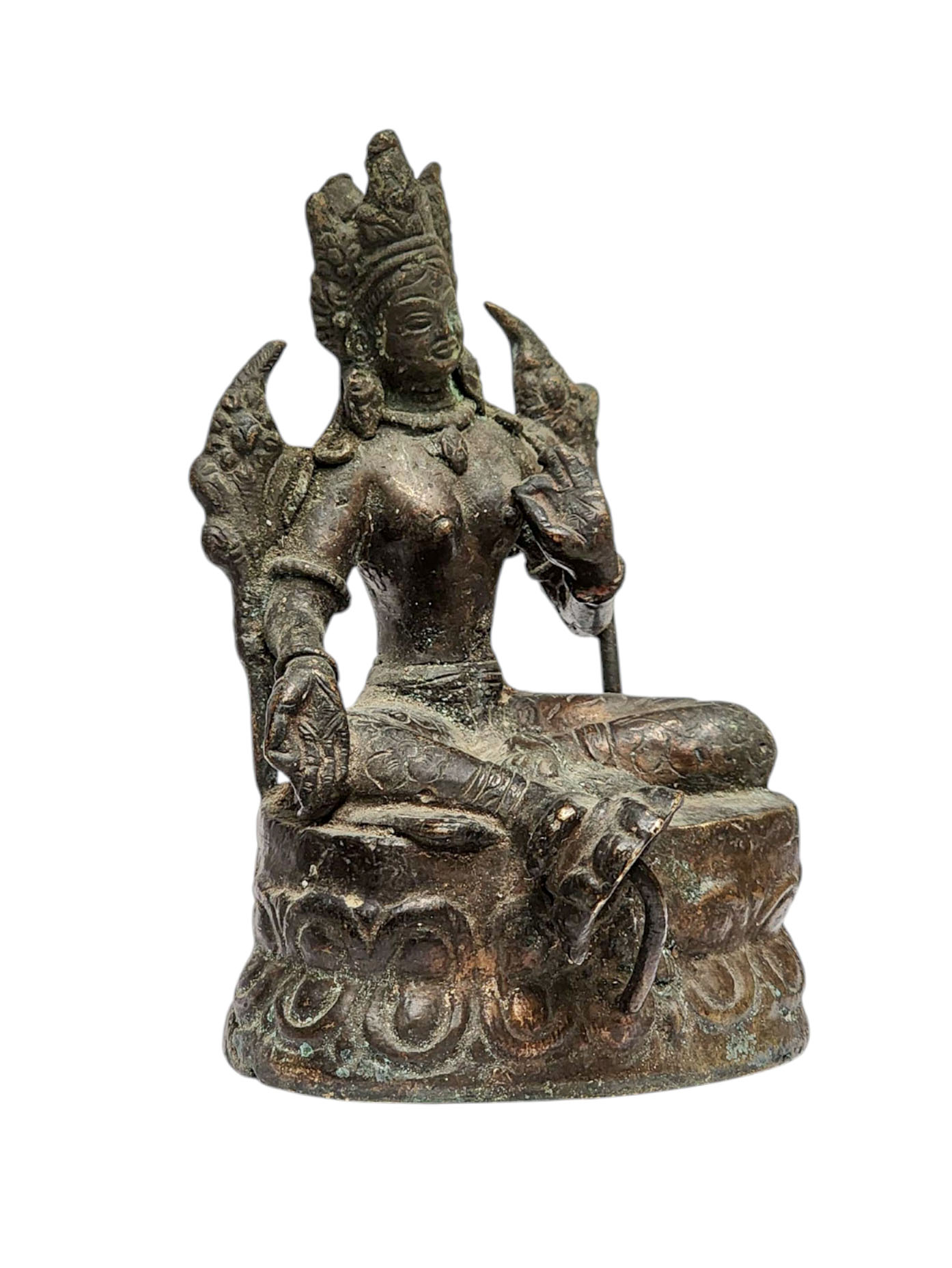  + 50 Year Old Buddhist Miniature Statue
+ 50 Year Old Buddhist Miniature Statue  Old Stock Statue
Old Stock Statue  Old Stock Statue
Old Stock Statue  Old, Buddhist Handmade Statue
Old, Buddhist Handmade Statue  Old, Buddhist Handmade Statue
Old, Buddhist Handmade Statue  Old, Buddhist Handmade Statue
Old, Buddhist Handmade Statue  Old, Buddhist Handmade Statue
Old, Buddhist Handmade Statue  Old Stock, Nepali Statue
Old Stock, Nepali Statue  Old Stock, Nepali Statue
Old Stock, Nepali Statue  of Ratnasambhava Buddha,
of Ratnasambhava Buddha,  of Ratnasambhava Buddha,
of Ratnasambhava Buddha,  Old, Buddhist Handmade Statue
Old, Buddhist Handmade Statue  Old, Buddhist Handmade Statue
Old, Buddhist Handmade Statue  Old Stock Statue
Old Stock Statue  Old Stock Statue
Old Stock Statue