Code
HCS4749
Weight
4 Kg / 8.82 lbs
Size
Height
30cm (12") Width
21cm (8") Depth
15cm (6") Material
Copper
Availability
Subject to Avilability
Date Added
2010-08-22 06:32:12
Note : We used to sell this product 15 years ago so it may no longer be in our stock.
It is possible that we still have it with our suppliers but the price could be different from before.
Feel free to order. We will verify availability and inform you promptly.
It is possible that we still have it with our suppliers but the price could be different from before.
Feel free to order. We will verify availability and inform you promptly.

Safe Payment
We accept Paypal, Money Transfer, Bank Transfer
Confidence
Protection covers your purchase and personal data.
Worldwide Delivery
We ship Worldwide, except Russia.Shipping cost US$25.2 for upto 0.5 kgs

Hotline
Talk to help line for your question on 9841267335Old Post : OLD POST
Please note that this Buddha Head Statue, [antique Finishing], [old Post], [remakable] is an old post. We typically do not remove our posts from the website for various reasons, such as nostalgia and maintaining page ratings. These posts are not intended for direct sales, but occasionally, we can remake the items.
Please note that this Buddha Head Statue, [antique Finishing], [old Post], [remakable] is an old post. We typically do not remove our posts from the website for various reasons, such as nostalgia and maintaining page ratings. These posts are not intended for direct sales, but occasionally, we can remake the items.
Remakable : Remakable
Please note that the Buddha Head Statue, [antique Finishing], [old Post], [remakable] we posted some time ago is not currently available in our store. However, due to the possibility of a remake, it is still on sale. The remake will not be an exact replica of the original statue shown in the picture and will require additional time to be ready for dispatch. If you are willing to wait for this custom remake, you may proceed with your order. Thank you for your understanding and patience.
Please note that the Buddha Head Statue, [antique Finishing], [old Post], [remakable] we posted some time ago is not currently available in our store. However, due to the possibility of a remake, it is still on sale. The remake will not be an exact replica of the original statue shown in the picture and will require additional time to be ready for dispatch. If you are willing to wait for this custom remake, you may proceed with your order. Thank you for your understanding and patience.
Bronze Finishing
This Buddha Head Statue, [antique Finishing], [old Post], [remakable] product features a stunning Bronze patina finish. Our store takes pride in offering this exclusive patina, which involves a meticulous process utilizing organic materials such as butter and vegetable color. The aim is to recreate the appearance of an aged bronze statue, evoking a sense of timeless elegance.
The art of giving the bronze color to red copper is truly exceptional and is practiced by skilled craftsmen. With each piece, you not only acquire a beautifully finished Buddha Head Statue, [antique Finishing], [old Post], [remakable] product but also pay homage to the artisans who are dedicated to preserving this rare and fading art form. The result is a unique and captivating aesthetic that adds a touch of sophistication and nostalgia to any setting. Read More . . .
This Buddha Head Statue, [antique Finishing], [old Post], [remakable] product features a stunning Bronze patina finish. Our store takes pride in offering this exclusive patina, which involves a meticulous process utilizing organic materials such as butter and vegetable color. The aim is to recreate the appearance of an aged bronze statue, evoking a sense of timeless elegance.
The art of giving the bronze color to red copper is truly exceptional and is practiced by skilled craftsmen. With each piece, you not only acquire a beautifully finished Buddha Head Statue, [antique Finishing], [old Post], [remakable] product but also pay homage to the artisans who are dedicated to preserving this rare and fading art form. The result is a unique and captivating aesthetic that adds a touch of sophistication and nostalgia to any setting. Read More . . .
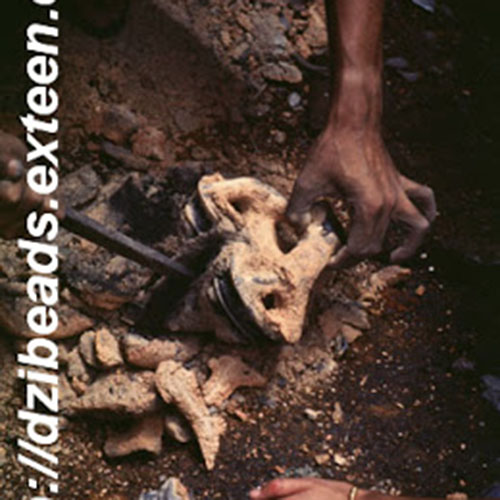
Lost-Wax System
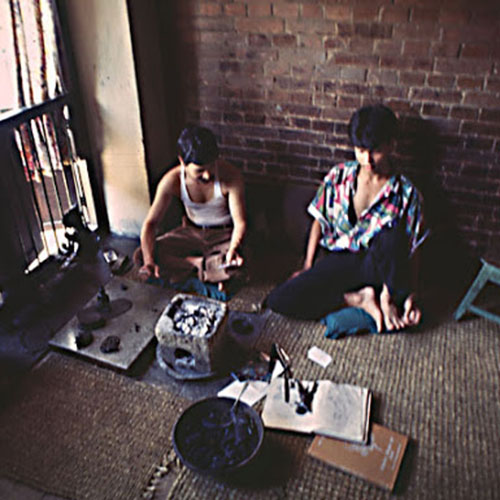
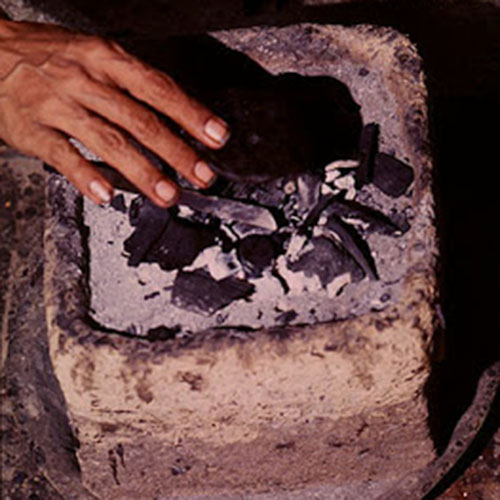
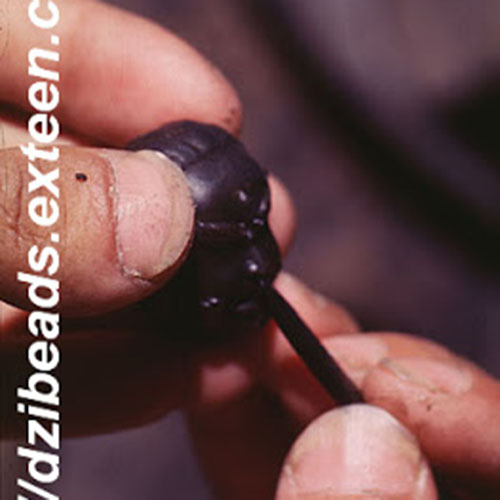
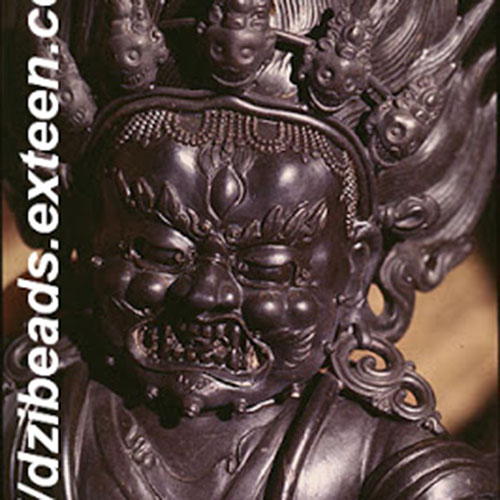
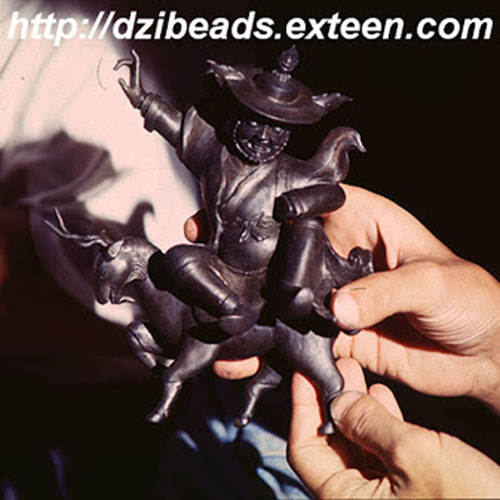
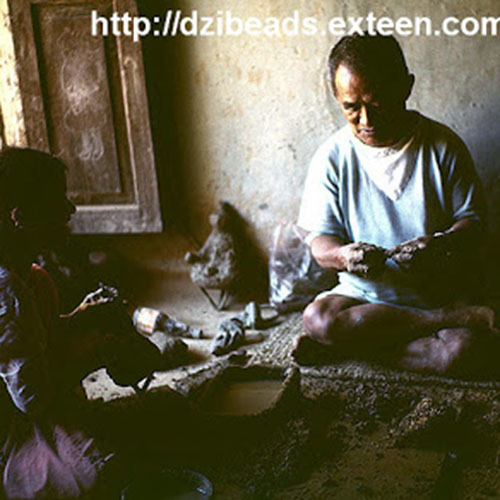
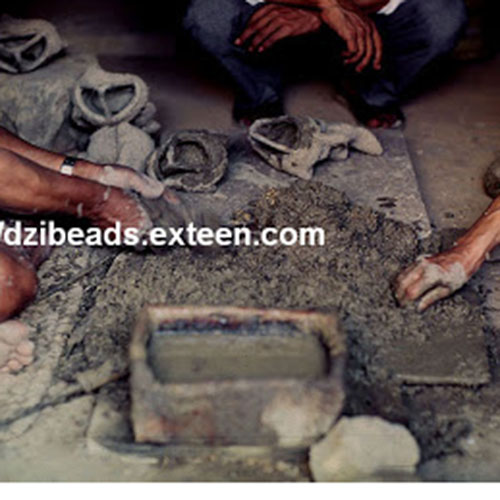
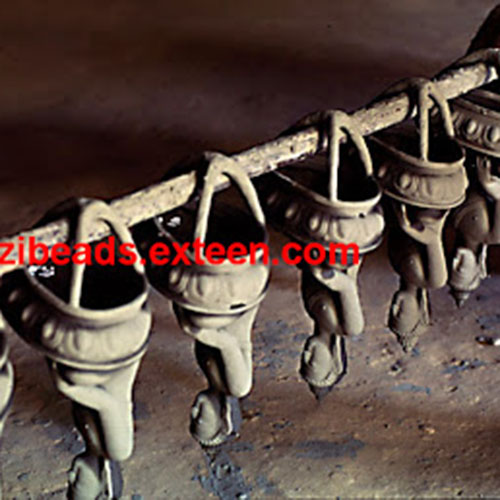
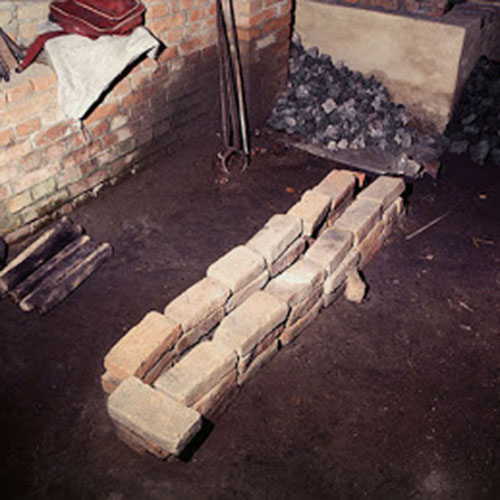
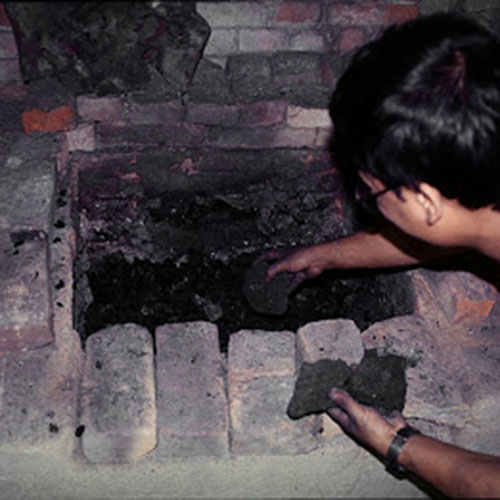
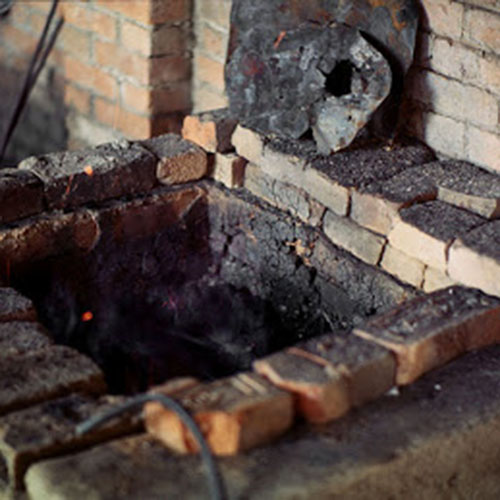
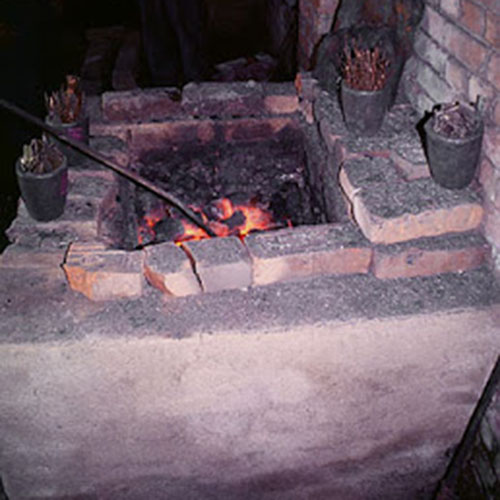
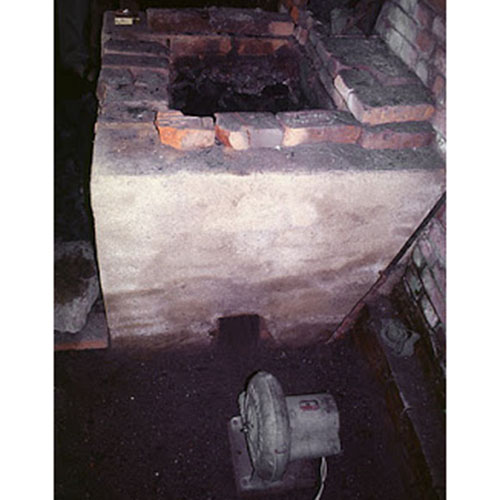
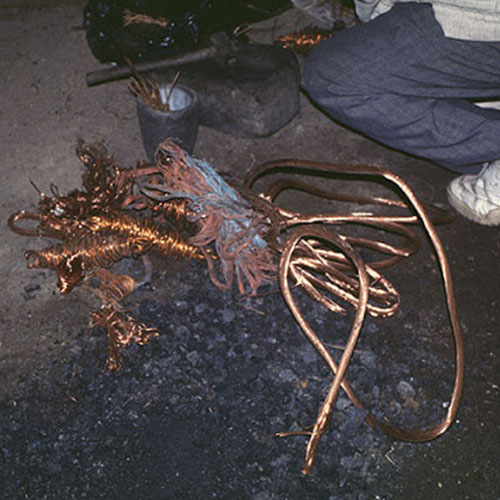
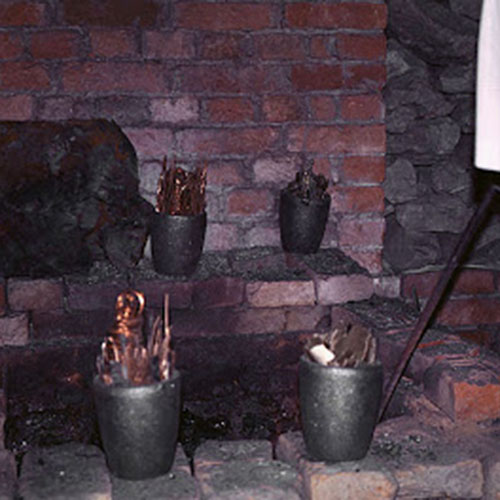
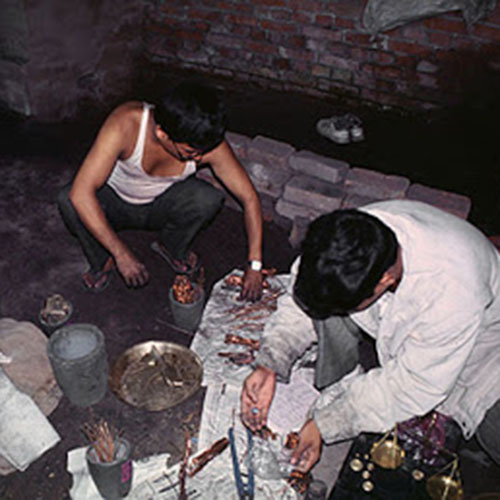
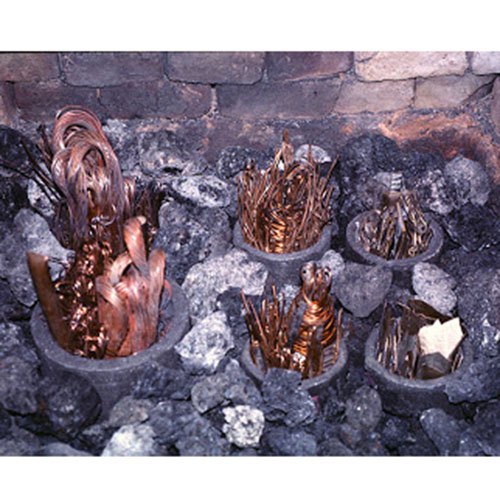
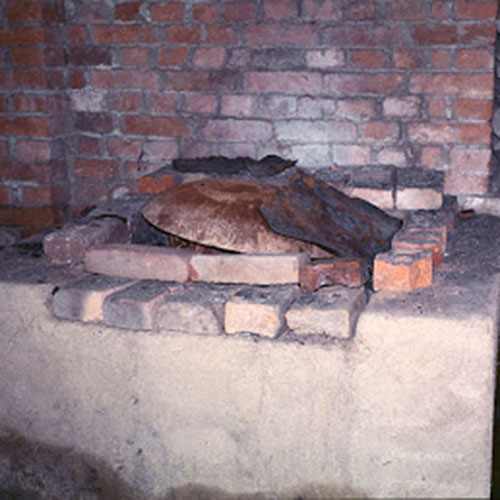
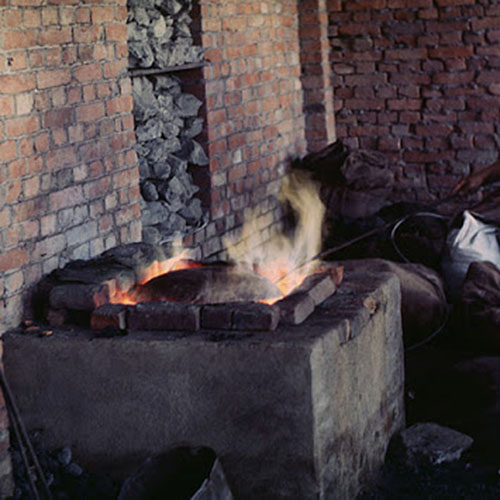
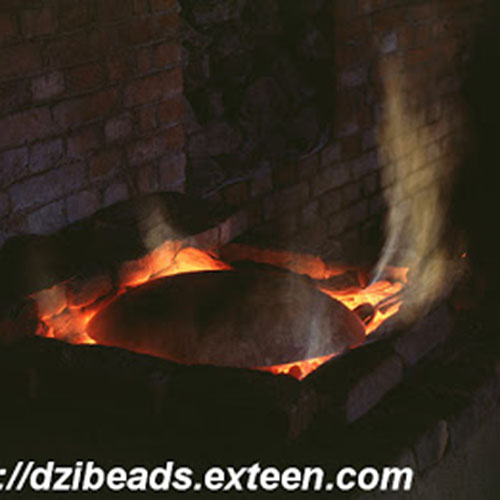
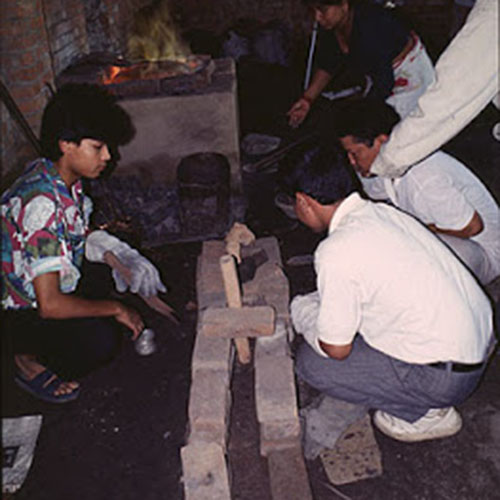
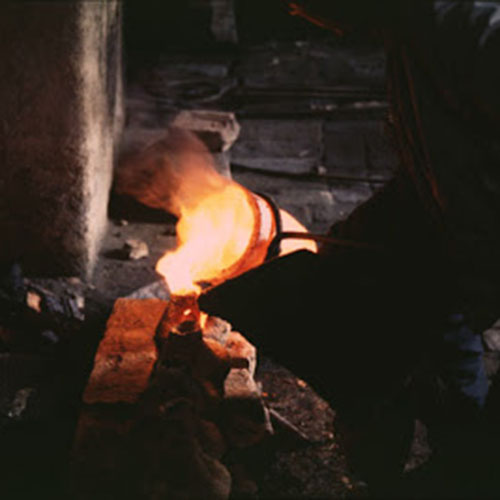
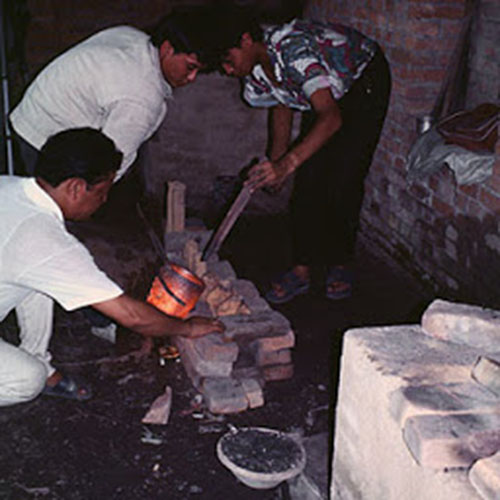
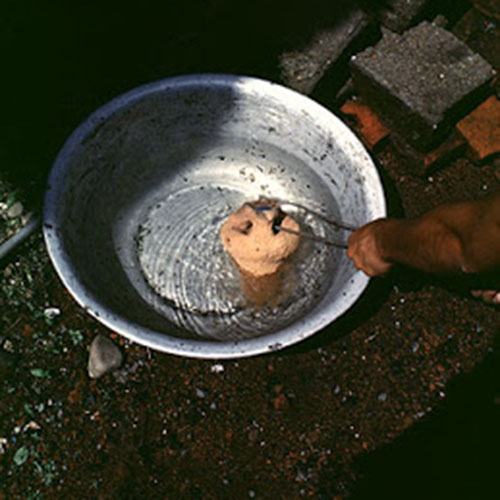
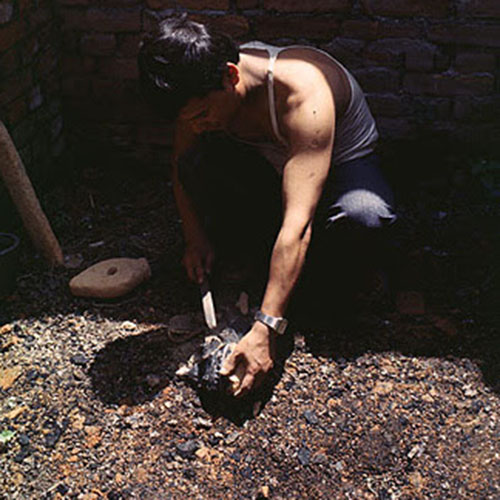
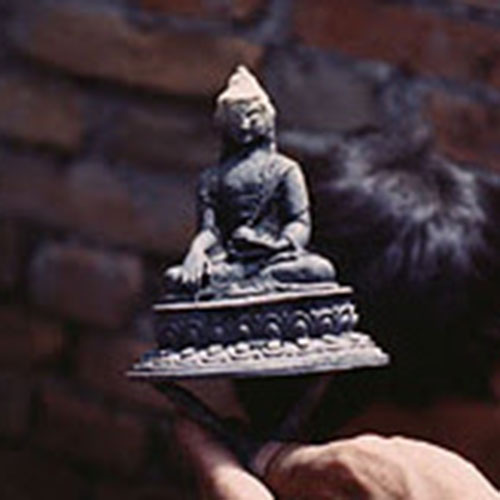
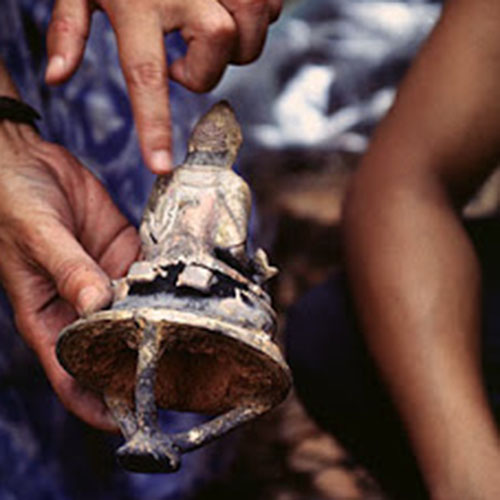
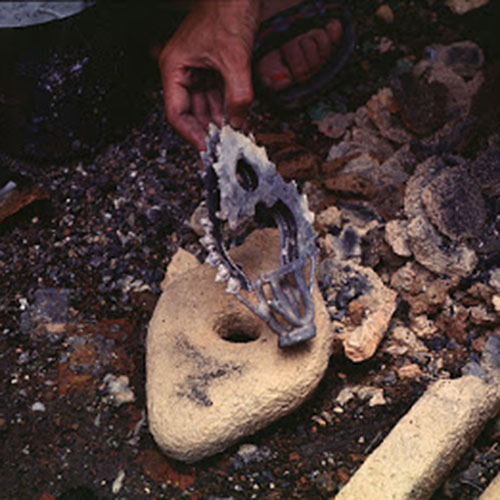
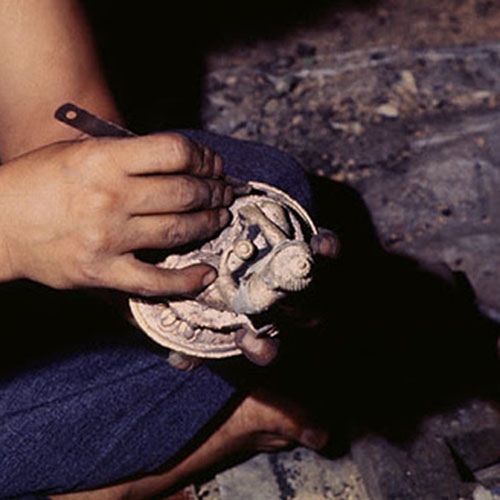
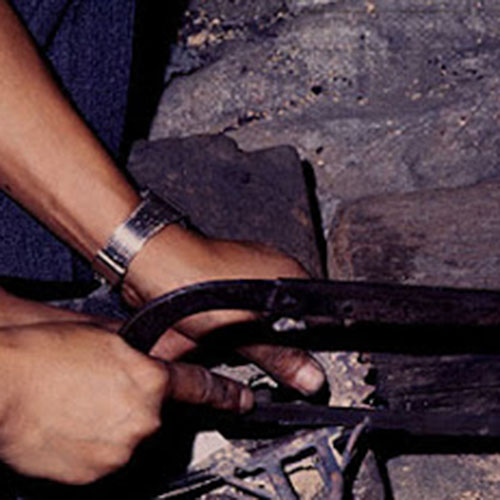
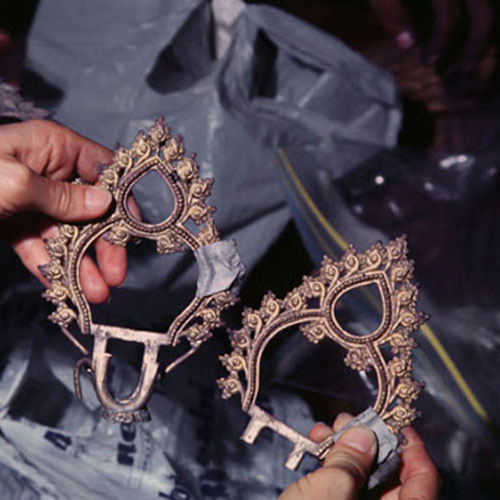
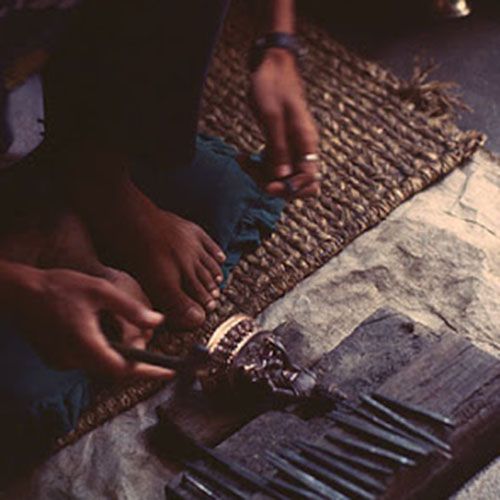
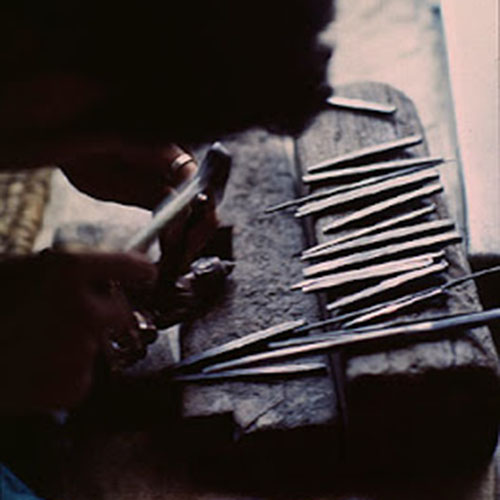
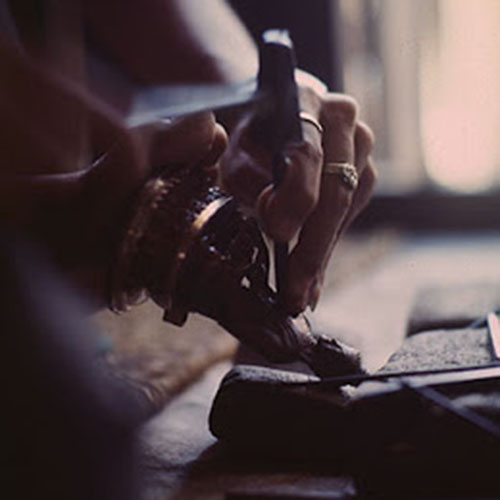
This Buddha of Buddha Head Statue, [antique Finishing], [old Post], [remakable] is made by the process of the Lost Wax system. This is a very complicated, time consuming and historic process of making metal sculptures.Which is why it is sometimes called Precision Casting as well. Hence the sculptures made by this process are comparatively expensive. There are many new, advanced and less time consuming methods of casting metal sculptures available as well. But due to the benefits provided by the traditional lost wax system in quality control and customization, we prefer the Loss wax system over Ceramic molding, or sand casting to make our Buddha.
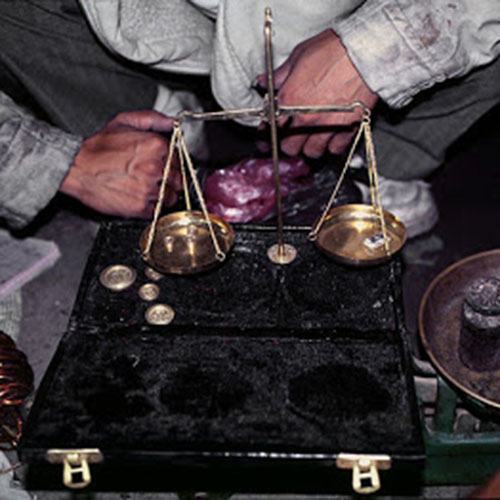
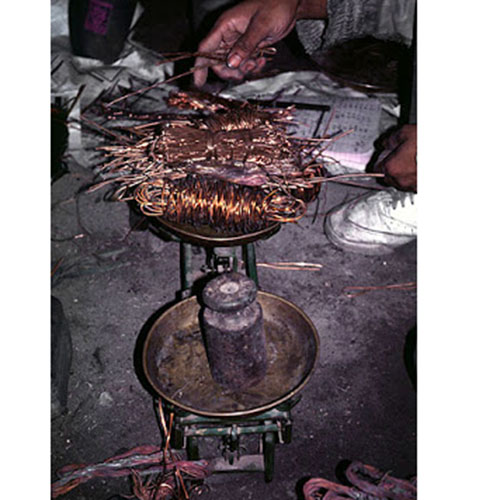
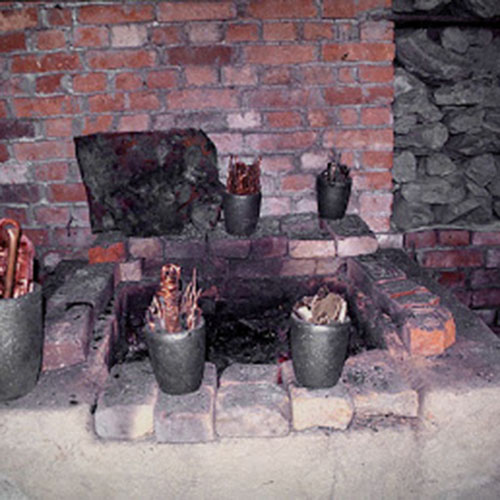
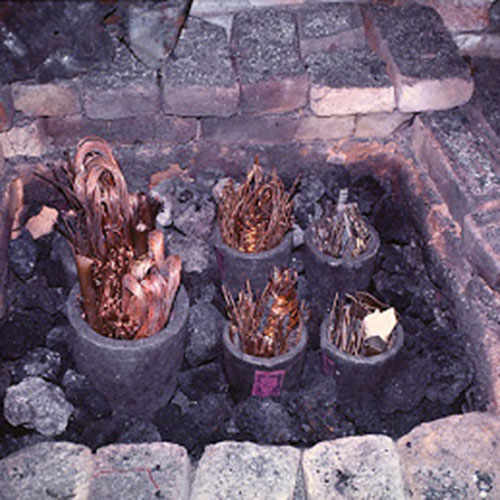
Below we have tried to illustrate the process of making a loss wax system statue: Read More . . .
This Buddha of Buddha Head Statue, [antique Finishing], [old Post], [remakable] is made by the process of the Lost Wax system. This is a very complicated, time consuming and historic process of making metal sculptures.Which is why it is sometimes called Precision Casting as well. Hence the sculptures made by this process are comparatively expensive. There are many new, advanced and less time consuming methods of casting metal sculptures available as well. But due to the benefits provided by the traditional lost wax system in quality control and customization, we prefer the Loss wax system over Ceramic molding, or sand casting to make our Buddha.
Below we have tried to illustrate the process of making a loss wax system statue: Read More . . .
About Buddha :
Gautama Buddha, popularly known as the Buddha, He is regarded as the founder of the world religion of Buddhism, and revered by most Buddhist schools as a savior, the Enlightened One who rediscovered an ancient path to release clinging and craving and escape the cycle of birth and rebirth. He taught for around 45 years and built a large following, both monastic and lay. His teaching is based on his insight into the arising of duḥkha and the ending of duhkha the state called Nirvana
The Buddha was born into an aristocratic family in the Shakya clan but eventually renounced lay life. According to Buddhist tradition, after several years of mendicancy, meditation, and asceticism, he awakened to understand the mechanism which keeps people trapped in the cycle of rebirth. The Buddha then traveled throughout the Ganges plain teaching and building a religious community. The Buddha taught a middle way between sensual indulgence and the severe asceticism found in the Indian śramaṇa movement. He taught a training of the mind that included ethical training, self-restraint, and meditative practices such as jhana and mindfulness. The Buddha also critiqued the practices of Brahmin priests, such as animal sacrifice and the caste system.
A couple of centuries after his death he came to be known by the title Buddha, which means "Awakened One" or "Enlightened One". Gautama's teachings were compiled by the Buddhist community in the Vinaya, his codes for monastic practice, and the Suttas, texts based on his discourses. These were passed down in Middle-Indo Aryan dialects through an oral tradition. Later generations composed additional texts, such as systematic treatises known as Abhidharma, biographies of the Buddha, collections of stories about the Buddha's past lives known as Jataka tales, and additional discourses, i.e. the Mahayana sutras.
A couple of centuries after his death he came to be known by the title Buddha, which means "Awakened One" or "Enlightened One". Gautama's teachings were compiled by the Buddhist community in the Vinaya, his codes for monastic practice, and the Suttas, texts based on his discourses. These were passed down in Middle-Indo Aryan dialects through an oral tradition. Later generations composed additional texts, such as systematic treatises known as Abhidharma, biographies of the Buddha, collections of stories about the Buddha's past lives known as Jataka tales, and additional discourses, i.e. the Mahayana sutras.


![Buddha Head Statue, [antique Finishing], [old Post], [remakable]](https://handicraftseller.com/uploads/pics/product/thumb/2010/08/4749.jpg)
![Buddha Head Statue, [antique Finishing], [old Post], [remakable]](https://handicraftseller.com/uploads/pics/product/thumb/2010/08/4749_0.jpg)
![Buddha Head Statue, [antique Finishing], [old Post], [remakable]](https://handicraftseller.com/uploads/pics/product/thumb/2010/08/4749_1.jpg)
![Buddha Head Statue, [antique Finishing], [old Post], [remakable]](https://handicraftseller.com/uploads/pics/product/thumb/2010/08/4749_2.jpg)






































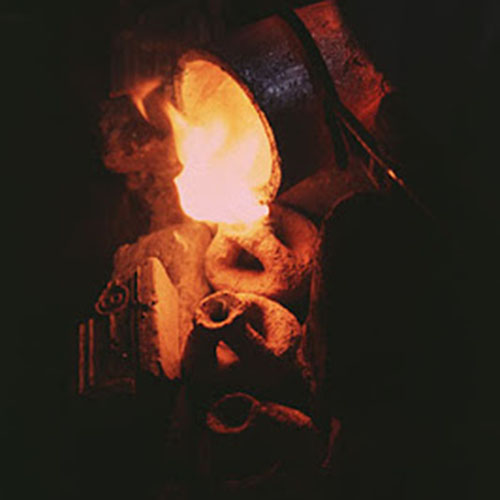


















 of Medicine Buddha
of Medicine Buddha  of Medicine Buddha
of Medicine Buddha  Stone Finishing,
Stone Finishing,  of Shakyamuni Buddha
of Shakyamuni Buddha  of Shakyamuni Buddha
of Shakyamuni Buddha  Amitabha Buddha,
Amitabha Buddha,  Amitabha Buddha
Amitabha Buddha of Medicine Buddha-
of Medicine Buddha-  of Medicine Buddha-
of Medicine Buddha-  Shakyamuni Buddha, Buddhist Handmade Statue,
Shakyamuni Buddha, Buddhist Handmade Statue,  Shakyamuni Buddha, Buddhist Handmade Statue,
Shakyamuni Buddha, Buddhist Handmade Statue,  of Medicine Buddha
of Medicine Buddha  of Medicine Buddha
of Medicine Buddha  Glossy,
Glossy,  Glossy,
Glossy,  Amitabha Buddha, Buddhist Handmade Statue,
Amitabha Buddha, Buddhist Handmade Statue,  Amitabha Buddha, Buddhist Handmade Statue,
Amitabha Buddha, Buddhist Handmade Statue,  Glossy,
Glossy,  Glossy,
Glossy,